If you want to integrate data annotation, inspection, and mining into your workflow you must use a technology that helps you with these tasks. In this article, we talk about an Image Classification API to do this.
Computer vision is described as the use of computers to automatically accomplish activities that the human visual system can perform. It refers to the process through which a computer can detect and interpret pictures using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and then construct an acceptable analytical result that the machine “understands.”
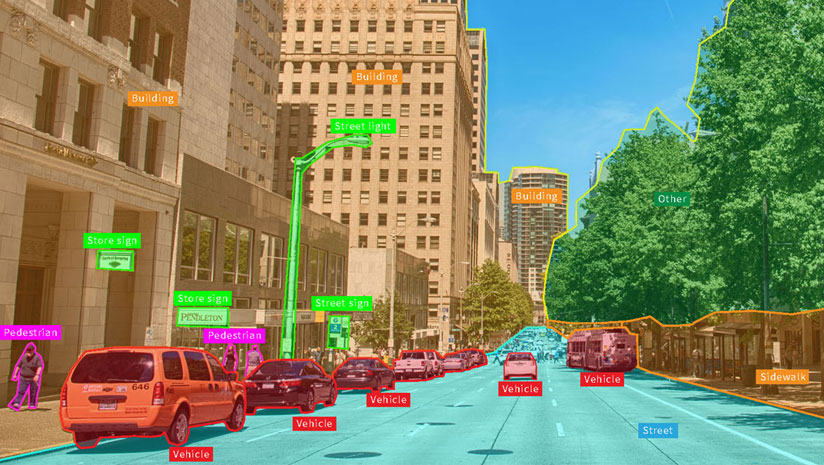
As a kind of artificial intelligence, it can categorize, identify, verify, and detect things, allowing robots to visually perceive their surroundings. This visual data is often in the form of images or movies, but it can also contain information from thermal and infrared cameras.
Computers employ digital cameras and build analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) and digital signal processing (DSP) methods to perform this task. They also employ a machine learning system that must be trained before it can effectively understand photos.
Machine learning techniques are utilized to train the algorithm that allows for better picture recognition. Constant training significantly improves the machine learning model’s prediction rate. The training data is used by algorithms to create associations, gain insight, make decisions, and measure their dependability.
However, there is an irrefutable correlation between correctly annotated data and the success of an artificial intelligence (AI) project: one researcher discovered that preparing, cleaning, and labeling data consumes up to 80% of development time. The significance of data annotation arises from the fact that even little inaccuracies can have major effects. Before they can begin to operate, self-learning algorithms require a huge amount of labeled data to train.
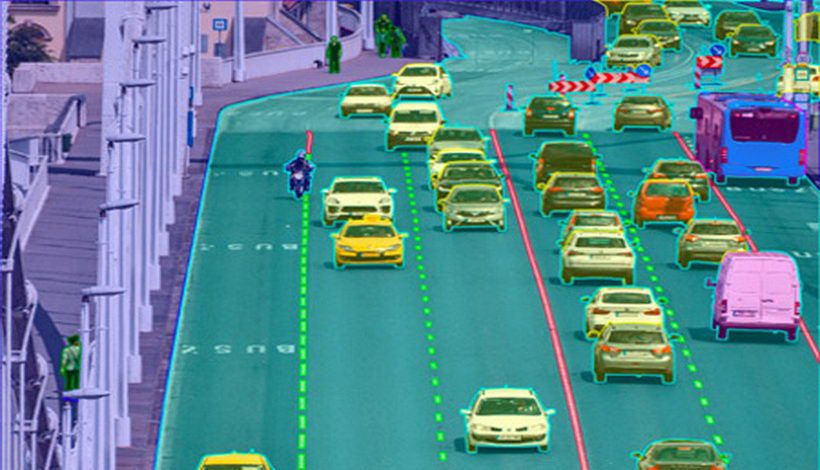
Image annotation is critical when discussing computer vision. This procedure tags images with appropriate task tags. To create extremely accurate training data, photographs should be annotated.
However, this activity cannot be completed by just anyone: expertise and contextual understanding, as well as mastery of certain approaches and instruments, are essential. Human resources, in summary, are key components of the data annotation process, especially when performing specific labeling activities.
When it comes to picture annotation, the natural tendency is to automate. Unsupervised machine learning, on the other hand, is not yet ideal for automatic image annotation since computers struggle to assign and recognize objects in pictures.
Manual human-driven picture annotation is more efficient in this scenario, and it also provides a scalable solution with quick turnaround times. Finally, it comes down to establishing the right mix of automation and human interaction for the individual project. You should use technologies to improve your workflow.
Use An API
An API is a program intermediary that lets unconnected programs connect (Application Program Interface). It acts as a bridge, accepting a demand or signal from one program and sending it to another, deciphering the messages, and carrying out protocols depending on the coding of the API.
APIs can be present in practically every aspect of our online activity: they are the hidden foundation of today’s world of plug-ins, digital displays, and software interaction. They connect everything and make sure that software systems function efficiently.
APIs are important in this respect since they allow us to create a range of purposes. In this scenario, manually analyzing a huge volume of picture data is a time-consuming effort that frequently does not produce the expected results. Use the Image Tagging Content API to assist you with data annotation, data mining, and workflow.
Why Image Tagging Content API?
Among the better APIs for this purpose is Image Tagging Content API. You may distinguish many items in photos, such as food and animals, as well as emotions in individuals. It supports a wide range of programming languages, which is why programmers prefer it daily.

