Did you know that you could get fluctuating data from Metals and in different programming formats? Do it through a metals JSON API!
Choosing which metal to invest in is one of the most challenging decisions for novice precious metal investors. The best metal is difficult to choose because each has different market and investment qualities. The fact that precious metal bullion exists in a variety of forms further complicates matters.
Here is a quick overview of the many precious metal investing options to assist you in choosing the best option for your individual investment portfolio.
Gold has long been a favorite among precious metals investors and has been used for thousands of years as a store of wealth. The reputation of gold as an investment that can withstand severe recessions and tends to keep its value well amid economic slowdowns. Compared to cash investments, gold is a superior hedge during times of rising inflation. Even though gold is a fantastic investment, some novice investors may find it difficult to afford to purchase sizable amounts of the metal.
When it comes to popularity among investors in precious metals, silver comes in second place only behind gold. Silver has the enormous benefit of being more affordable than gold, which makes it simpler to start with a little sum of money and create a portfolio from scratch by making minor deposits on a regular basis over time. The vast usage of silver in industry, notably in the quickly expanding solar energy industry, supports the metal’s price. Despite its benefits, silver can be difficult to store due to its lower cost when compared to other precious metals.

The industrial, manufacturing, and ornamental uses of copper are numerous, and the market is broad. Copper has a finite supply and is in high demand, just like other precious metals. Although compared to gold and silver, copper is sometimes neglected as an investment, more and more investors are beginning to acquire copper bullion coins and bars to protect their portfolios against future currency deflation.
JSON Programming
For individuals who are committed to the precious metals investing industry, several platforms are devoted to receiving from banks or other financial institutions financial data on the movements and prices of metals. Also, some of this platforms give the option to chose different programming formats, like JSON Programming.
JavaScript Object Notation, or JSON. JSON is a compact data storage and transmission format. When data is transferred from a server to a web page, JSON is frequently utilized. JSON “self-describes” and is simple to comprehend. Some websites, like Metals-API system is suggested of using this programme.
Get Into Metals-API
When Metals-API first debuted, it was a straightforward, small API for banks’ current and historical precious metals prices. The Metals-API API may offer real-time precious metals data through API with a precision of two decimal places and a frequency of up to every 60 seconds.
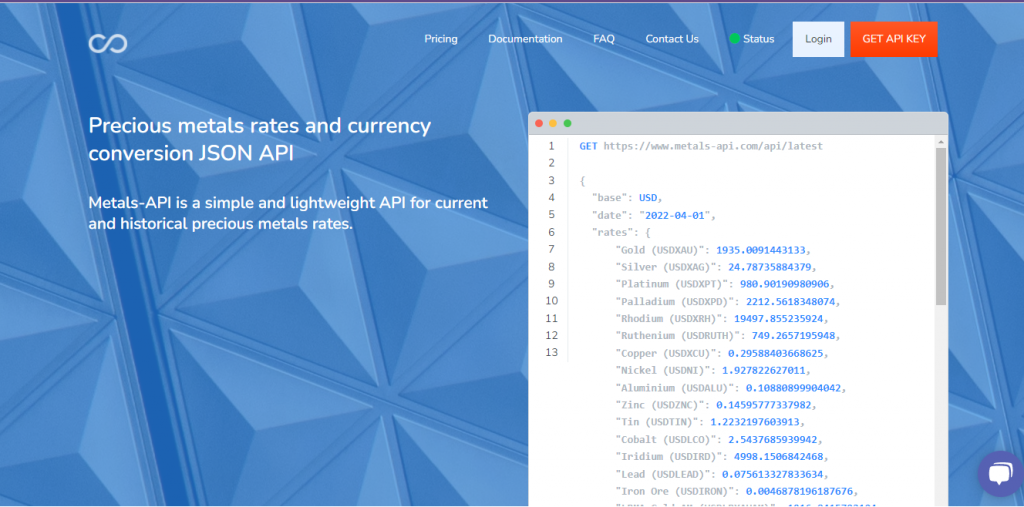
A few of the features on Metals-API include the ability to convert between different currencies, the provision of time-series data, volatility statistics, and the lowest and highest prices of each day.
Approaches to Use
Metals-API is simple to use. Now all you have to do is adhere to these guidelines.
1. Create a profile to get started.
2. Establish an API Key.
3. Choose the proper metal and currency of your desire.
4. Request an API through the system and wait for it to respond.
A Lucrative Platform
Every day, Metals-API.com is used by tens of thousands of programmers, small and medium-sized enterprises, and large corporations. Metals-API is the best source for current precious metals rates because to its reliable data sources and more than six years of expertise.
A Trustworthy Website for Their Clients
Banks and organizations that provide financial information, like the European Central Bank, are where Metals-API gets its currency data from. Your connection to the Metals-API API is encrypted using bank-grade 256-bit SSL encryption.
The 256-bit encryption technique is used to encode and decode data or files. It is the third-strongest encryption technique used by the majority of modern encryption algorithms, protocols, and technologies, after 128-bit and 192-bit encryption.

